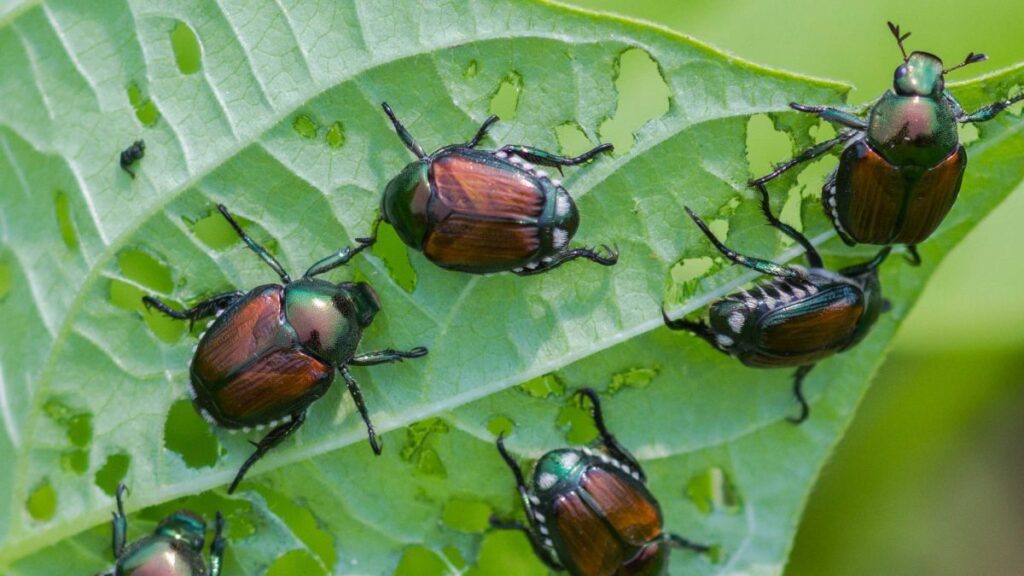
As we approach the summer months, one of the most notorious pests that arborists and gardeners must prepare for is the Japanese beetle. Known for their voracious appetite and wide host range, these beetles can cause significant damage to a variety of plants. This spotlight will delve into the life cycle, phenology markers, and management strategies for dealing with Japanese beetles.
Life Cycle and Identification
The Japanese beetle is a member of the Scarabaeidae family. Adult beetles are easily recognizable by their metallic green bodies and copper-brown wing covers. Measuring about ½ inch in length, these beetles emerge from the ground in late June to early July, with peak activity typically around the July 4th weekend.
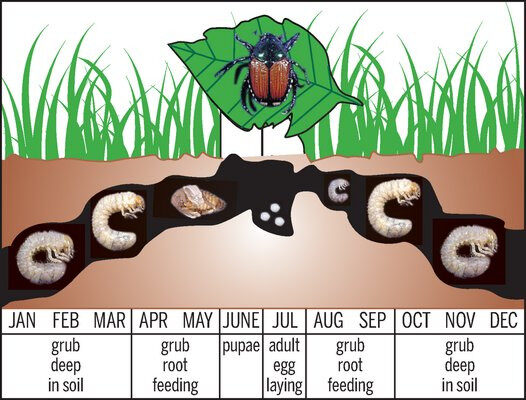
Their life cycle begins with eggs laid in the soil by females during the summer months. The eggs hatch into white grubs that feed on grassroots, causing damage to lawns and turf. These grubs overwinter in the soil and pupate in the spring, emerging as adults in the early summer. The entire life cycle takes about one year to complete.
Phenology Markers and Degree Days
Tracking the emergence of Japanese beetles can be effectively managed using phenology markers and Growing Degree Days (GDD). Japanese beetle emergence typically occurs at approximately 1,000 GDD (base 50°F). This timing often coincides with the bloom of linden trees and roses, making these plants excellent indicators for the impending arrival of Japanese beetles.
Additionally, the July 4th weekend serves as a reliable calendar marker for peak adult beetle activity in many regions. This period is critical for monitoring and initiating control measures.
Damage and Impact
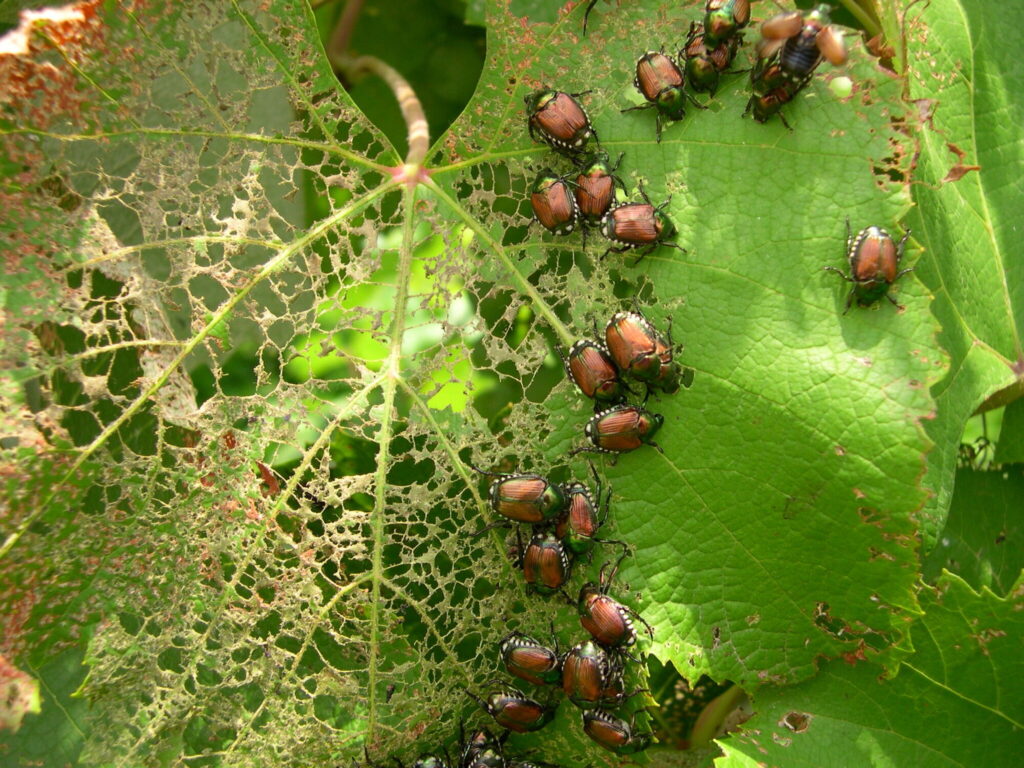
Japanese beetles are polyphagous, meaning they feed on a wide range of plant species. They are particularly fond of roses, grapevines, linden trees, and various fruit trees. The damage caused by adult beetles includes skeletonizing foliage, leaving only the leaf vein intact. This type of feeding can severely weaken plants, reducing their ability to photosynthesize and increasing their susceptibility to other stresses.
The grubs, on the other hand, damage lawns and turf by feeding on grassroots, leading to dead patches of grass that can be easily pulled up. This root damage can be extensive, especially in well-irrigated lawns.

Control Measures
Effective management of Japanese beetles requires an integrated approach, combining cultural, mechanical, biological, and chemical methods.
- Cultural Controls:
- Maintaining healthy, well-irrigated lawns can help reduce the impact of grub feeding. Healthy turf is more resilient and better able to recover from damage.
- Planting less susceptible plant species can reduce the attractiveness of your garden to Japanese beetles. Some plants that are less favored by these pests include begonias, lilacs, and boxwoods.
- Mechanical Controls:
- Handpicking adult beetles and dropping them into soapy water can help reduce their numbers. This method is most effective in the early morning when beetles are less active.
- Installing physical barriers, such as fine netting or row covers, can protect vulnerable plants from beetle feeding, particularly during peak activity periods.
- Biological Controls:
- Beneficial nematodes and Milky Spore disease can be applied to soil to target and reduce grub populations. These biological agents are safe for use around humans, pets, and beneficial insects.
- Chemical Controls:
- Insecticides can be used to control both adult beetles and grubs. Products containing carbaryl, imidacloprid, or pyrethroids can be effective, but it is important to follow label instructions and apply these treatments judiciously to minimize harm to non-target organisms.
- Soil-applied systemic insecticides can provide longer-lasting protection against grubs. These should be applied in late spring or early summer before the grubs have caused significant damage.

The Japanese beetle is a persistent and damaging pest that requires vigilance and a multifaceted management strategy. By understanding their life cycle, monitoring phenology markers like Growing Degree Days and bloom times, and employing a combination of control measures, you can effectively protect your plants and turf from these voracious insects. As we approach the July 4th weekend, keep an eye out for these shiny invaders and be ready to take action to mitigate their impact. For expert assistance in managing Japanese beetles and other plant health care needs, call Homer Tree Care. Our certified arborists are here to help you protect and maintain the health of you landscape.

