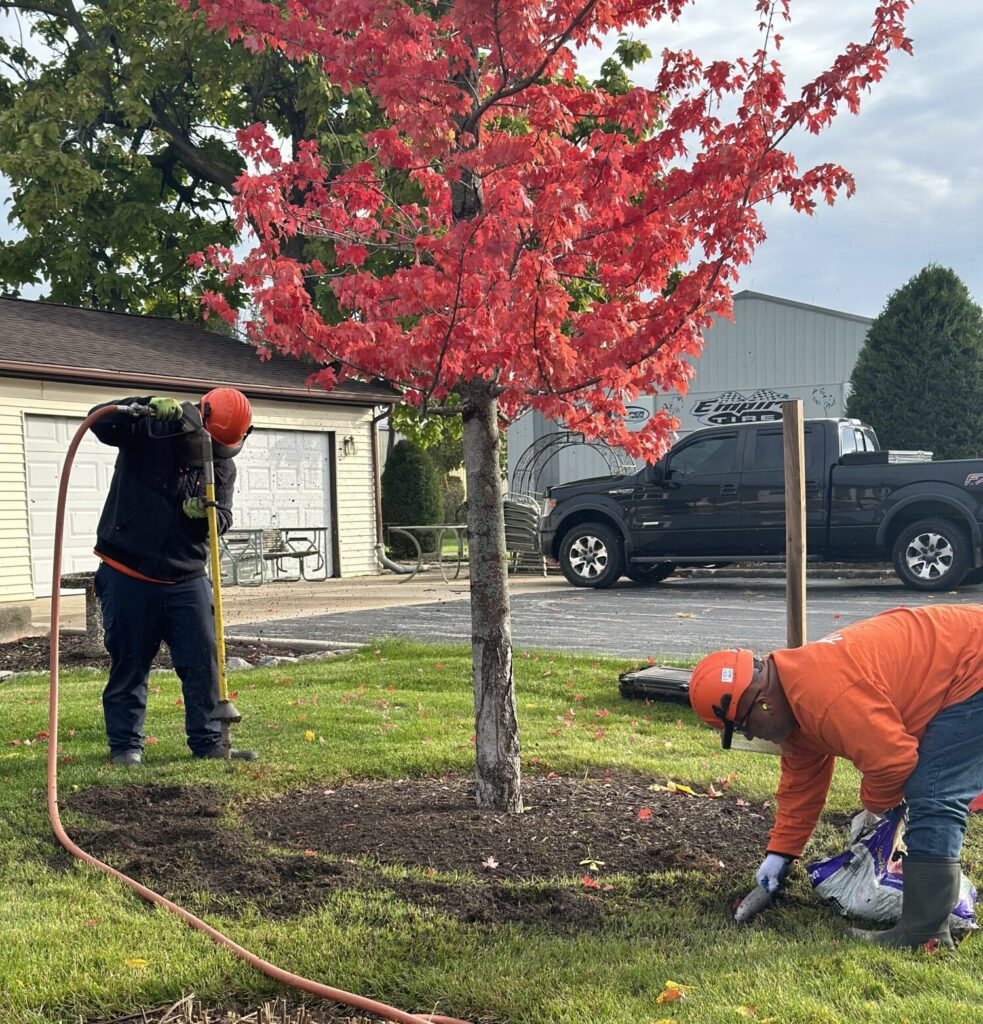
Healthy soil is the foundation for robust tree growth, providing essential nutrients, oxygen, and support for the development of a strong root system. However, when soil becomes compacted, it poses a significant threat to the well-being of trees. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the concept of soil compaction, its impact on tree development, and effective remediation techniques that Homer Tree Care recommends for maintaining thriving trees.
What is Soil Compaction and How is it Measured?
Soil compaction refers to the compression of soil particles, reducing the pore spaces between them. One common method for measuring soil compaction is through bulk density. Bulk density is the mass of soil per unit volume, and it is a key indicator of how densely packed the soil is. The higher the bulk density, the more compacted the soil, limiting the movement of air, water, and nutrients.
The Impact of Soil Compaction on Trees:
- Restricted Root Growth: Compacted soil hinders the expansion of a tree’s root system. As roots struggle to penetrate the dense soil, their growth becomes stunted, limiting their ability to absorb water and nutrients essential for the tree’s survival. This often leads to the formation of shallow surface roots, which can make trees more susceptible to environmental stressors and limit their overall stability.
- Reduced Oxygen Supply: Soil compaction decreases the amount of oxygen available to tree roots. Oxygen is crucial for root respiration and nutrient uptake. Without an adequate oxygen supply, trees may exhibit signs of stress, such as yellowing leaves, stunting growth, and increased susceptibility to diseases.
- Impaired Water Infiltration: Compacted soil has reduced porosity, inhibiting water infiltration. This can lead to poor drainage and, conversely, waterlogged conditions during periods of heavy rainfall. Both scenarios can be detrimental to tree health, causing root rot and other water-related issues.
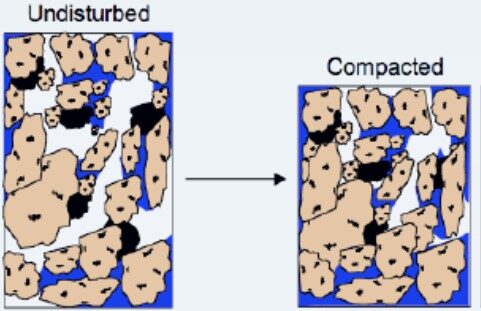
Remediation Strategies for Soil Compaction
Understanding the importance of addressing soil compaction is the first step toward promoting tree health and longevity. Here are effective remediation strategies that can mitigate the adverse effects of compacted soil:
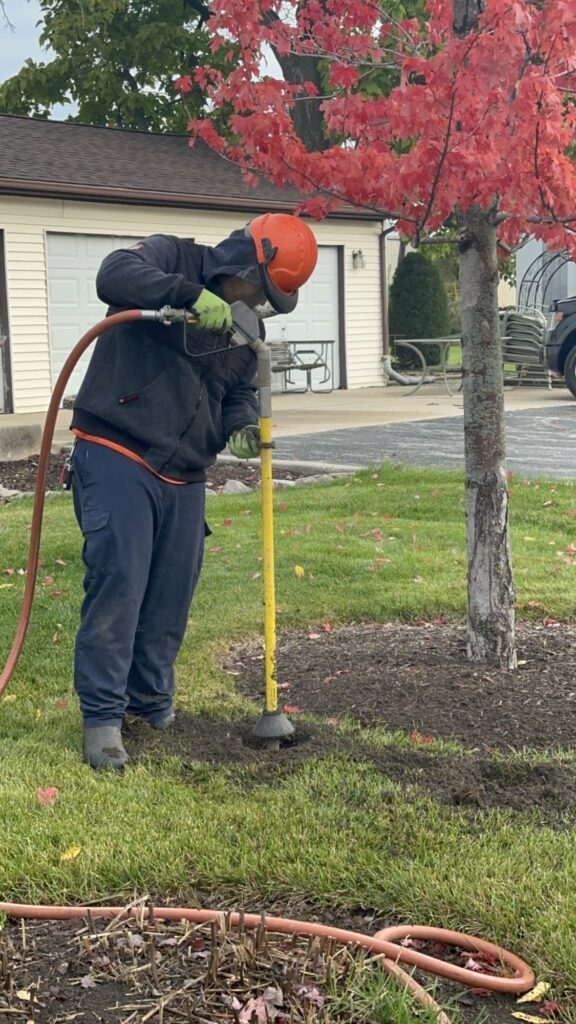
- Root Zone Decompaction: Some traditional methods like radial trenching have been employed for soil compaction remediation, but we advocate for a more effective and less invasive approach – root zone decompaction using the air spade. Unlike trenches that disrupt the root structure, the air spade method involves mechanically blowing soil apart under the canopy, ensuring a more comprehensive and less disruptive process.
- Vertical Mulching: Vertical mulching entails drilling holes into the compacted soil and filling them with organic matter, such as compost or wood chips. This improves soil aeration, water infiltration, and nutrient availability. Vertical mulching is particularly effective in urban environments where soil compaction is common.

- Avoiding Heavy Machinery: Preventing soil compaction in the first place is crucial. When undertaking construction or landscaping projects, minimize the use of heavy machinery and establish designated areas to protect the root zones of existing trees.
Connecting Remediation Techniques to Homer Tree:
At Homer Tree Care, we specialize in comprehensive tree care services that prioritize the well-being of your trees. Our expertise includes mulching to improve soil quality gradually and air spade decompaction for more immediate relief from soil compaction issues. In a previous blog post, we explored the benefits of air spade decompaction in detail. To order mulch for your trees, visit Homer Industries.
Maintaining healthy soil is fundamental to ensuring the well-being of trees in any landscape. By understanding the impact of soil compaction and implementing effective remediation strategies, we can preserve the beauty and functionality of trees for generations to come. Homer Tree Care is committed to fostering a deep appreciation for the intricate relationship between soil health and tree vitality, offering expert guidance to nurture thriving landscapes.

